Welcome to another episode of The Literacy Bug Podcast! This week I respond to the recent blog entry called “Encoding, Decoding and Understanding (Print) Language”. In the mentioned blog entry, I casually glossed over the importance of oral language comprehension in the role of literacy development. In glossing over oral comprehension, I did not neglect or undermine its significance. In fact, I acknowledge the complexity and significance of language comprehension in propelling the need to encode and decode anything in the first place. In this podcast, I explore that which was left unexplored: the intricate relationship between print processing, language development and cognitive processing. Please listen, explore and enjoy! We aim to bring many more episodes in the coming weeks. (theliteracybug.com)
In the Spirit of Wittgenstein: Seeking a Clear View of Literacy
Following on the heels of the most recent blog entries (here and here), we have another unpublished entry to share from the archives … Unpublished no more, though. Whilst there are some rough edges to it, it is posted here as part of the ongoing conversation
Preamble
Often, when I have had a picture well framed or have hung it in the right surroundings, I have caught myself feeling as proud as if I had painted the picture myself. That is not quite right: not as proud as if I painted it, but as proud as if I had helped to paint it, as if I had, so to speak, painted a little bit of it. It is as though an exceptionally gifted arranger of grasses should eventually come to think that he had produced at least a tiny blade of grass himself. (Wittgenstein, Culture & Value)
Following in the tradition of Ludwig Wittgenstein, I am compelled to grasp a clear view (or perspicuous representation) of literacy. It is a view that is not encumbered by the various forms and instances of literacy. In the spirit of Hans Sluga (2011), the search represents a compulsion to articulate a surveyable representation of an unsurveyable whole. The unsurveyable whole - in this case - is the history of the written word and its current manifestations in print and digital form.
While this might seem an esoteric preamble to an otherwise basic blog entry, I was not comfortable proceeding without a nod to the context to these words.
Literacy Facts
Here are the elements of a clear view of literacy in English.
1. There are 26 letters in the English alphabet.
- 21 are consonants;
- 5 are vowels (or 6 if you treat “y” as a sometimes vowel)
2. We use these letters and letter combinations to represent 44 phonemes or English sounds (give or take one or two).
- 25 consonant sounds
- 19 vowel sounds
The clever reader will notice a curious fact about consonant and vowel sounds; there is a greater letter-sound correlation in relation to consonant sounds than there is for vowel sounds. It isn’t as easy to explicitly state the various letter and letter combinations which represent the 44 phonemes in English. These are learned over time, and are analysed from the learner’s growing (print) vocabulary. For more information, please refer to to the charts below.
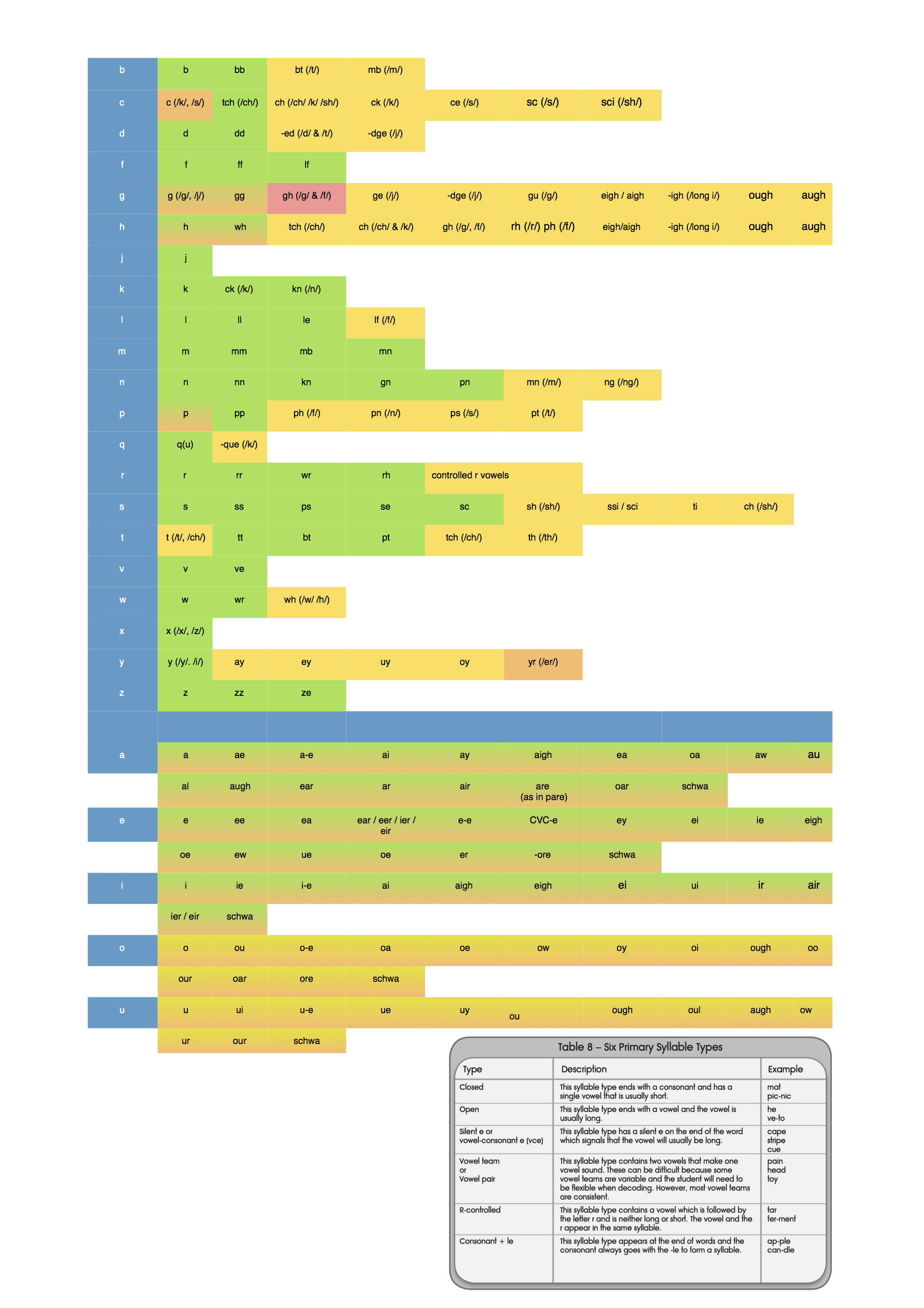
3. There are also 131 possible graphemes which represent those 44 or so phonemes. There are 74 possible consonant graphemes to represent the 25 consonant sounds, and 57 vowel graphemes to represent the 19 vowel sounds. A grapheme can be an individual letter (like the letter "k") or it can be a group of letters (like the grouping "igh", "ph" or "ea"). And a grapheme can make more than one sounds. For example, the letter "a" can make four different sounds, as in cat, baby, father, alone. The letter "a" makes two sounds in the common word "banana". Can you identify the sounds? The following diagram shows a mapping of the 44 phonemes and all the grapheme which can represent those sounds.
Learners do not recognise all graphemes from the get go. In terms of learning, the following is a recommended order in which children explore the various graphemes in the first three to four years of school.
- Letter Name-Alphabetic (Semi-Phonetic) Stage [typically between 4 - 7 yrs old]: CVC word patterns with the following sequence of graphemes and blends: a, m, t, s, i, f, d, r, o, g, l, h, u, c, b, n, k, v, short e, w, j, p, y, x, q, z, sh, ch, th, wh, st-, pl-, bl-, gl-, sl-, sp-, cr, cl, fl, fr, sk, qu, nk, ng, mp, ck
- Within Word (Transitional) Stage [typically between 7 - 9 yrs old]: CVCe word patterns leading into more complex CVVC vowel patterns and common multisyllabic words: a-e, ai, ay, ei, ey, ee, ea, ie, e-e, i-e, igh, y, o-e, oa, ow, u-e, oo, ew, vowel+r, oi, oy, ou, au, ow, kn, wr, gn, shr, thr, squ, spl, tch, dge, ge, homophones
4. These sounds/graphemes are joined to form syllables. There are six common syllable types in English.
- Closed (e.g. mat or pic/nic)
- Open (e.g. he or ve/to)
- Silent “e” or vowel-consonant-e [vce] (e.g. cape or stripe)
- Vowel team or vowel pair (e.g. pain, head or toy)
- R-controlled (e.g. far or fer/ment)
- Consonant+le (e.g. a/pple or li/ttle)
In an analytic phonics approach, learners analyse known words to gain a firm grasp of letter-sound correspondences and word patterns. In a synthetic phonics approach, learners progressively move through letter-sound patterns of increasing complexity. Both approaches should be systematic, developmental and integrated. In practice, both approaches should be used, though one approach may be more or less dominant or effective.
5. Over time, we notice how …
- The larger a learner’s vocabulary, the more lexical items the learner has to draw on to comparatively see how words work;
- Phonological and phonemic awareness places an individuals in a position to problem solve the aural structure of words, and hold this in working memory for encoding and decoding;
- Morphological knowledge helps a learner refine options by seeing meaningful, regular patterns in words;
- Emerging spelling rules are understood through further practice;
- Eventually, knowledge is built up over countless encounters with words. Some words we just remember. Other words we decode, encode and recognise in context.
5. Word level fluency is not enough to engender reading/writing fluency, though. Learners must also become adept at rapidly interpreting, scanning and generating the grammatical elements in our sentences.
- We must identifying the components of syntax, and understanding how the logic of this syntax allows one to express states of affairs and to understand states of affairs expressed in utterances.
- This includes the ability to track pronouns - for instance.
- The structure of a sentence explains how elements are related to one another (e.g. The cow jumped over the moon). This includes an awareness of the various types of words (e.g. nouns, verbs, adjectives, etc).
- We need to know the words to extract sense from the sentence. And we often need to grasp the intention/conversation of the sentence to grasp its meaning.
To consolidate: Structural features are mastered whilst an individual is in the early stages of learning language and literacy. Whilst the learner is learning, teachers are directing the learner’s attention to the way in which language is represented in print.
Proceed With Caution
It is here that we need to proceed with caution.
The above (meta-linguistic) knowledge is necessary but not sufficient for full literacy development. It represents the form of our utterances but not their content. Actual utterances have content (i.e. refer to things and are parts of conversations).
Actual statements are also more complex than the formulaic syntax learned in formal grammatical study. Actual utterances include nuances of idiomatic language, fragmented constructions, rhetorical devices and more.
The sequence of statements in a texts are also shaped by a dialogic agreement between “speaker” and “audience” … rather than a formulaic one which is determined by the structure of the utterance on its own. For instance, when Michael Mohammed Ahmed writes in his novel The Tribe (2014):
“Most of my Tayta’s children still live with her in a house that belonged to my grandfather. His name was Bani Adam. Everyday my father reminds me that it was my grandfather's house, he says, ‘We are Baat Adam,’ which means, ‘We are the House of Adam’. The house is in Alexandria. People sometimes think because we’re Arabs, that I mean the city in Egypt, but the Alexandria we’re from is actually a suburb in Sydney's inner-west.” (p. 3-4)
The sequence of the text responds to the imagined needs of an imagined interlocutor rather than a logic inherent in the grammatical form of the text. The text abides by the conventions of autobiography whilst anticipating questions/assumptions that an audience would be making. (Note: Even a recipe is shaped by the conventions/expectations imposed by tradition/context.)
This observation is most pronounced in the otherwise mimetic text - a poem by William Carlos William
“so much depends
upon
”a red wheel
barrow
“glazed with rain
water
“beside the white
chickens.”
Whilst simple on its surface, the poem demands its audience to see beyond the merely descriptive poem. The author would like the audience to appreciate its meditative quality if the text is to communicate as intended. One must recognise how the poem may or may not fit within the tradition of the haiku. (Note: See this as an example of Wittgenstein’s ‘language game’ concept illustrated in the video at the end of this section.)
We get close to a mimetic portrait in Ernest Hemingway’s “Big Two-Hearted River”, but even “Big Two-Hearted River” requires its audience to be familiar with the general context, the language/vocabulary, and the overtones of Romanticism.
“Nick looks down into the pool from the bridge. It was a hot day. A kingfisher flew up the stream. It was a long time since Nick had looked into a stream and seen trout. They were very satisfactory. As the shadow of the kingfisher moved up the stream, a big trout shot upstream in a long angle, only his shadow marking the angle, then lost his shadow as he came through the surface of the water, caught the sun, and then, as we went into the stream under the surface, his shadow seemed to float down the stream with the current, unresisting, to his post under the bridge where he tightened facing up into the current.” (p. 143-144)
Ludwig Wittgenstein was a philosopher obsessed with the difficulties of language, who wanted to help us find a way out of some of the muddles we get into with words.
Coda
Whilst the surface code can be teased out as an object of analysis, the content of utterances elicits background knowledge which is so pervasive that any analysis must acknowledge that
“nothing merely physical, such as acoustic blasts or ink marks, or even words and gestures - ‘signs’ of one kind or another - can possibly communicate thought. For such tokens taken by themselves are ‘dead’, and can only be animated, have life breathed into them, by something inner, such as an act of understanding.” (Stern, 2004, pg 136)
Schneider (2014) also notes this implicit and confounding dilemma. Any formulaic, analytic theory of meaning makes only so much progress through a focus on structure alone. Eventually, one must include the imagination/experience/context/shared language of the speaker and the audience as part of the equation.
Formal theories of meaning seek to explain how propositions express a sense, hopefully clearly and unambiguously, through an understanding of the proposition’s logical structure. In such a case, one must have access to the phonetic, orthographic, syntactic and lexical knowledge to be able to decode the sentence and to decipher the picture expressed within the sentence. This process is quite a static exchange. Wittgenstein himself was inspired by Gottlob Frege to contribute to the formalist, analytical project in the Tractates Logico-Philosophicus, but would soon find this pursuit inadequate to explain how meaning is expressed beyond a very limited frame.
Wittgenstein found that meaning - in context - is less static and more elusive. The meaning of an utterance requires an understanding of the utterance’s context, a familiarity with the way the utterance is being exchanged, the intentions of the participants, and the position of the utterance within a “language game” or “conversation”. For instance, the meaning of the phrase “he is a Red” could meaning “He is a communist”, “He is a supporter of the Liverpool Football Club”, “He is a Native American”, or some other derivative. Its meaning is dependent on factors outside of the logical structure of the utterance itself. For another example, let's say someone said, "I really loved Madagascar." The individual could be referring to the place, the film or Madagascar vanilla (as opposed to another type of vanilla). There might be an audience who wouldn't find the phrase ambiguous (they only know one meaning for Madagascar) or it might not be meaningful at all (they have no concept of Madagascar whatsoever), even though they understand the grammar of the sentence and can accurately pronounce each element.
Therefore, actual elements of context, content, purpose, practice, deliberation and cognitive/information processing must be dealt with to leap into meaning. This does not negate the importance of direct, explicit instruction in the structural elements of language and literacy; however, we must acknowledge that formal skills only facilitate communication. They are not the germ of communication.
In the words of Ludwig Wittgenstein
A. TLP 3.13: A proposition includes all that the projection includes, but not what is projected. Therefore, though what is projected is not itself included, its possibility is. A proposition, therefore, does not actually contain its sense, but does contain the possibility of expressing it. (‘The content of a proposition’ means the content of a proposition that has sense.) A proposition contains the form, but not the content, of its sense.
B. Z 74: A sentence is given me in code together with the key. Then of course in one way everything required for understanding the sentence has been given me. And yet I should answer the question “Do you understand this sentence?” : No, not yet; I must first decode it. And only when e..g. I had translated it into English would I say “Now I understand it.”
C. PI 496: Grammar does not tell us how language must be constructed in order to fulfil its purpose, in order to have such-and-such an effect on human beings. It only describes and in no way explains the use of signs.
D. Z 91: Ask: What result am I aiming at when I tell someone: “Read attentively”? That, e.g. this and that should strike him, and he be able to give an account of it. — Again, it could, I think, be said that if you read a sentence with attention, you will often be able to give an account of what has gone on in your mind, (e.g. the occurrence of images). But that does not mean that these things are what we call “attention”.
E. TLP 3.141: A proposition is not a blend of words. — (Just as a theme of music is not a blend of notes.) A proposition is articulate.
F. CV: Often, when I have had a picture well framed or have hung it in the right surroundings, I have caught myself feeling as proud as if I had painted the picture myself. That is not quite right: not “as proud as if I painted it, but as proud as if I had helped to paint it, as if I had, so to speak, painted a little bit of it. It is as though an exceptionally gifted arranger of grasses should eventually come to think that he had produced at least a tiny blade of grass himself.
G. PI 291: What we call “descriptions” are instruments for particular uses. Think of a machine drawing, a cross-section, an elevation with measurements, which an engineer had before him. Thinking of a description as a word-picture of the facts has something misleading about it: one tends to think only of such pictures as hang on our walls: which seem simply to portray how a thing looks, what it is like. (These pictures are as it were idle.)
H. PI 533: How can one explain the expression, transmit one’s comprehension? Ask yourself: How does one lead anyone to comprehension of a poem or of a theme? The answer to this tells us how meaning is explained here. Let’s simplify language to the declarative statement that has the capacity to convey the unambiguously.
I. “I shall in the future again and again draw your attention to what I shall call language games. There are ways of using signs simpler than those in which we use the signs of our highly complicated everyday language … If we want to study the problems of truth and falsehood, of the agreement and disagreement of propositions with reality, of the nature of assertion, assumption, and question, we shall with great advantage look at primitive forms of language in which these forms of thinking appear without the confusing background of highly complicated processes of thought.” (quoting Wittgenstein in Monk, 2005, p 69)
J. “When the boy or grown-up learns what one might call specific technical languages, e.g. the use of charts and diagrams, descriptive geometry, chemical symbolism, etc. he learns more language games. (Remark: The picture we have of the language of the grown-up is that of a nebulous mass of language, his mother tongue, surrounded by discrete and more or less clear-cut language games, the technical languages … Here the term ‘language game’ is meant to bring into prominence the fact the speaking of language is part of an activity, or a form of life …” (Wittgenstein quoted in Phillips, 1977, pp 29 - 31)
K. “The pupil must want to go on alone in taking language to the world, and that what is said must be worth saying, have a point (warning, informing, amusing, promising, questioning, chastising, counting, insisting, beseeching, specifying the location of pain, and so on), then is there some question left as to whether the pupil has to find warning, informing, amusing, promising, counting, beseeching, chastising, and so on themselves worth doing? If it is part of teaching to undertake to validate these measures of interest, then it would be quite as if teaching must, as it were, undertake to show a reason for speaking at all.” (Cavell, 2005, pg 115)
References
Literary References
Ahmad, M. M. (2014). The Tribe. Western Sydney (NSW): Giramondo.
Hemingway, E. (1995). The Collected Stories (Everyman's Library Classics). New York: Everyman's Library.
Williams, W. C. “The Red Wheelbarrow” n.d. Web at https://www.poets.org/poetsorg/poem/red-wheelbarrow.
Wittgenstein References
Wittgenstein, L. (1967). Zettel (Z). (G. E. M. Anscombe & G. H. von Wright, Eds.). Berkeley, CA: University of California Press.
Wittgenstein, L. (1974). Philosophical Grammar (PG). (R. Rhees, Ed.). Berkeley, CA: University of California Press.
Wittgenstein, L. (1980). Culture and value (C&V). Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Wittgenstein, L. (2001a). Philosophical Investigations (PI) (3rd ed.). Oxford, UK: Blackwell Publishing.
Wittgenstein, L. (2001b). Tractatus logico-philosophicus (TLP). London: Routledge.
Academic References
Cavell, S. (2005). Philosophy the day after tomorrow. In Philosophy the day after tomorrow (pp. 111 – 131). Cambridge, MA: Belknap Press.
Phillips, D. (1977). Wittgenstein and scientific knowledge. London: Macmillan Publishers Limited.
Schneider, H. J. (2014). Wittgenstein’s later theory of meaning: imagination and calculation. Oxford, UK: John Wiley & Sons.
Sluga, H. (2011). Wittgenstein. Oxford, UK: Wiley-Blackwell.
Stern, D. (2004). Wittgenstein’s Philosophical Investigations: an introduction. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
The Machinery of Language and Literacy
In light of the most recent blog entry - Encoding, Decoding and Understanding (Print) Language - I've gone back to the archives to revisit an unpublished piece from the past. Whilst there are some rough edges, it is posted here as part of the ongoing conversation.
Introduction
The layout of the diagram to the lower right might seem odd when it starts with “the world” as the notion at the top and "form of life" at the bottom, but this is to suggests that language and literacy are learned in a particular context. And the context determines the language(s) one speaks and it determines what one is likely to speak about.
In the words of Wittgenstein and Tomasello we find:
“When a child learns language it learns at the same time what is to be investigated and what not.” (Wittgenstein, On Certainty #472)
“‘Nothing could seem less remarkable than a one-year-old child requesting ‘More juice’ or commenting ‘Doggie gone’ … From an ethological perspective, perhaps the most astounding fact is that something on the order of 80 percent of all Homo sapiens cannot understand these utterances at all.” (Tomasello, 2003, pg 1)
Let’s say English is a language that is spoken in this environment. And - let’s say - that the word “Madagascar” exists in this world, and I hear the word “Madagascar” uttered in this place of the world. It also refers to a film (that I haven’t seen, but am aware of) and it is a type of vanilla (Madagascar vanilla), which I don’t know much about, either. There is a history to the word, and this history is its meaning. One points to a map to show me where the country is. One offers to watch a film with me. And one shows me a picture of Madagascar vanilla, and - perhaps - I have a chance to taste it. As long as I know that places, films and plants have names, then it is possible that I can know what is being referred to.
Phonological Awareness & Phonemic Awareness
I ask someone to say the word slowly, so I can have a go at writing the word, because if one is going to recognise the printed word, one must first be phonologically and phonemically aware of the word.
When I listen closely, I notice that Madagascar has four syllables:
Ma / da / ga / scar
One must also distinguish each of the sounds within the word:
[/m/+/short a/] + [/d/+/schwa/] + [/g/+/short a/] + [/s/+/k/+/ar/]
Alphabetic Principle, Phonics & Spelling
Then I attempt to spell the word based on my knowledge of English graphemes
M = /m/
a = /short a/
—
d = /d/
a = /schwa/
—
g = /g/
a = /short a/
—
s = /s/
c = /k/
ar = /controlled vowel - ar/
I’m pretty confident the opening letter is M to represent the /m/ sound, since I intuitively know that the letter “m” represents the /m/ sound most of the time (94% of the time to be accurate, if you see the chart to the right/above). Similarly, I know the /short a/ sound when I hear it. Whilst the letter “a” represents the /short a/ 96% of the time, I only appreciate this from experience. To make a long story short, I know the word “scar” and intuit that the word ends with the same spelling. I could be wrong, but this is when one’s word knowledge helps one problem-solve new words. That said, I might have spelled it incorrectly, and I might need to consult someone or something (e.g. a dictionary) to see if I am on the right track.
In the end, I heard a word, and I used my phonemic awareness skills to isolate the sounds. I used my knowledge of sounds-letters and my knowledge of words to spell it. If I didn’t have any of these attributes then I could be overwhelmed by the length of the word, etc. But I wasn't. Phew!
Morphology
For the time being, let’s say I recognise the word and I know that there is nothing quite morphological about the proper noun Madagascar. There are no meaningful prefixes, roots or suffixes which would assist me.
In a Sentence
Do we ever really encounter words only in isolation, though? As noted by Wittgenstein,
“If I know an object (word) I also know all its possible occurrences in states of affairs. (Every one of these possibilities must be part of the nature of the object/word.)” (Wittgenstein, Tractatus Logico-Philosophicus, #2.0123)
In this case, I read the following state of affairs:
Madagascar is an island country in the Indian Ocean.
I am lucky. I know English grammar, and I am familiar with all the words - when spoken - but I struggle with the written form of the printed word “island”. I am familiar with the spoken word, which is pronounced
[/long i/] + [/l/+/short a/+/n/+/d/]
But I don’t know about this
[/short i/+/s/+/l/] + [/short a/+/n/+/d/]
But a helpful person informs me that the letter “s” is indeed silent, and the opening letter “i” is a /long i/ syllable. In fact, the printed word “island” is familiar in the end. What a relief?
Sentences in Context
I know the sentence is a descriptive sentence, and I know that it is meant to convey information. I use my background knowledge to place the sentence in context. This sentence comes next:
The population of Madagascar is over 22 million people, and it spreads over 500,000 square kilometres.
I recognise that the emerging paragraph is a geography paragraph and I anticipate that I’ll find out about the capital city of Madagascar, primary industries, natural sites and cultural practices. I know this because I am familiar with this genre of discourse, and I expect and value this knowledge. I intuitively am comparing this with a similar text I read/heard/wrote earlier. The earlier one was about the island of Taiwan, and I am interested to know the differences between the two island contexts. If I didn’t have this previous experience or background knowledge, then I might not be able to read/hear/write the new text as deeply or critically.
Another Attempt
Let us look at another set of words. Let’s imagine that a friend shows me a photo of a red wheelbarrow sitting in the rain and provides with the following poem:
“so much depends
upon
”a red wheel
barrow
“glazed with rain
water
“beside the white
chickens.”
“It’s beautiful,” she says. “It’s by a fellow named William Carlos William.”
I’m not really fussed by the poem, to be honest. And I don’t know why it starts with the phrase “so much depends / upon”. But my friend insists that the poem is meaningful. Even though I know all the words, and I can understand/imagine the scene, I am missing something. So my friend asks me to bring in a photo of something that is significant to me. When we meet again, we both come armed with a photo. My photo is of my late grandmother, and her photo is of a pier jutting out into a river at dusk. She reads out her poem.
“so much depends
upon ...
"the smell of
the river
"of bait, of fish
and blueberries
"on hot summer
days."
And she helps me write mine:
“so much depends
upon
"my grandmother's
photo
"on the mantle
piece
"watching over
me."
We do it again next week, and the week after, and I start to get the point. I find it peaceful just stating something meaningful. My friend and I might talk about the “meaningfulness” of the object in the photo, but these "meanings” or even descriptions are left unsaid in our poems. At some stage, she introduces me to haikus, and I find that I have a new way to relax. Every so often I stop and write or think or say “so much depends upon …” I didn’t understand the point at the start but I do now, and I have started to branch out into other forms/purposes of poetry. I’m really quite surprised. In fact, it takes on a form of meditation or secular prayer. Whilst I still need to draft reports and memos at work, I have another written outlet that extends what I achieve in print. I have learned a new "language game" - so to speak.
Conclusion
Let’s return to the opening diagram, and we find the following:
- We live in a world;
- And in that world there are “things”, “concepts”, “phrases”, “relationships”, etc;
- These “things” have words, whether they are physical, like “a rock”, or conceptual, like "kindness”;
- Some of these words are functional and appear in phrases or as single words, like “How are you?” and “therefore”;
- The words are strung together in sentences to express some sense/meaning, and those sentences are strung together as part of a discourse of some kind;
- And we communicate about something in some way to others.
To end, let me present the following scenarios:
- an experienced electrician is wiring up a new electrical system. The electrician knows what everything is called and what everything does, but quivers when someone hands him an installation manual full of words and abstract schematics. “Mate, I can’t makes heads or tales of that thing” as he points to the manual. “I know what I’m doing.” Is it the technical nature of the manual that catches him off guard?
- a philosopher is asked to wire up a new electrical system. The philosopher has no clue about electronics and quivers at the sight of the wires. Someone hands him an installation manual full of words and abstract schematics. After much effort, the philosopher eventually says, “Mate, I can’t makes heads or tales of that thing” as he points to both the manual and the box of wires.
- an average person who is familiar with electronics, but is in no way an expert or practiced, is asked to wire up a new electrical system. She has a strong grasp of literacy and she is able to process information accurately. She knows what NOT to do in relation to voltage and amperage. She is eventually able to get the job done with the help of the manual, a few YouTube videos, and a couple calculated phone calls.
How would you go about explaining what is occurring in each of these scenarios? You may use the following diagram to help.
References
Tomasello, M. (2003). Constructing a language: a usage-based theory of language acquisition. Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
Wittgenstein, L. (2001). Tractates Logico-Philosophicus. Translated by D.F. Pears and B.F. McGuinness. London: Routledge.
_____________. (1969). On Certainty. Edited by G.E.M. Anscombe and G.H. von Wright. Translated by D. Paul and G.E.M. Anscombe. New York: Harper Torchbooks.
Encoding, Decoding and Understanding (Print) Language
Introduction
Please permit me to be abrupt ... at the start, at least. Isn't literacy merely the encoding, decoding and understanding of language? Simplistic though it may sound, print is the younger cousin of the much older member of the family.
The above schematic addresses this rough relationship between language and literacy. If one is developing the components of language - e.g. phonological, lexical, morphological, grammatical, textual and pragmatic skills - then the learning of “the code” serves to facilitate the transference of the learner’s speech into print, which itself can serve as a platform upon which further literate language can be built. In this case, the code is the interface between language and literacy, and this code requires that learners develop additional skills in order to coordinate and manipulate language-in-print.
From an early age, a child is learning language, but this child will only slowly develop an awareness of print. By age 6, a child will know thousands of words in oral language, but only know a few - if any - when read (Chall, 1996). This rich oral language provides ample stimulus for learners to begin exploring known (oral) words in print. In the coming years, the child’s oral language will continue to be stronger than what he/she can express on the written page. It is only at 13 years of age that your skilled readers are as competent in oral language as they are in literacy. By 15 to 17 years of age, print (finally) overtakes oral language. At this stage, a learner is apt to be better equipped to explore complex ideas on the page than verbally, particularly if the learner has a strong corpus of academic language. Across this prolonged developmental period, learners become increasingly more adepts and fluid in navigating and representing ideas in literate language.
The remainder of this entry will sketch some thoughts that may come to impact how we approach the encoding, decoding and understanding of literate language. I enter into the discussion with a profound appreciation of print’s older cousin, even though we will not discuss the specific uses of language here.
Part One: Encoding
WORDS [EITHER AUDIBLE OR INAUDIBLE] ---> DIVIDED INTO SYLLABLES & SOUNDS ---> ENCODED WITH GRAPHEMES ---> RECONSTRUCTED INTO PRINT WORDS [WORDS THAT I RECOGNISE]
Isn't it logical to analyse known words, and harness a learner's phonemic awareness to become adept at anticipating how to spell such-and-such a word which is already familiar to the learner? And - then - provide scaffolded opportunities for learners to monitor their own speech to use this skill in their emerging writing? Can't we leverage oral language and visual prompts as vehicles through which the learners become curious about words, the sounds in words and how these sounds and words are represented in print?
These are my queries in relation to the following possible lesson sequence, which could be considered an analytical approach to language-in-print:
- A known word is uttered orally;
- That word is segmented into syllables and phonemes (evidenced by phonemic awareness);
- The learner identifies the matching phoneme cards (pictured below);
- The learner has a go at spelling the word based on emerging sound-to-letter knowledge (invented spelling);
- That spelling is tested against the word's conventional spelling, which opens up a platform for discussion of common patterns;
- We return to the meaning of the word, and of using the word in context.
If a child can recognise all the letters of the alphabet (26 items), what's stopping him or her from memorising all possible English phonemes (45 items, give or take one or two)? And then using this knowledge to "phonemically spell" words that are part of the learner's oral language vocabulary? Sounds logical to me.
We ask kids to memorise the alphabet. Why don't we ask children to remember and apply all possible phonemes in English?
This is effective up to a point. The learner becomes adept at monitoring external and internal speech, and the learner develops a process to more rapidly represent this speech in print. Over time, the learner will process this information more rapidly as he/she recognises certain words and word patterns as whole units. For the time being, the learner is discovering the language-to-print connection, which is a step toward the writing-to-reading connection.
Part Two: Decoding
Eventually, the tables are turned, though. It is no longer enough to be able spell words by relying upon the stimulation of internal and external speech. The learner will need to decode words that are presented first in print. The learner will need to derive oral language from print, which will require that he or she recognises regular patterns, such as phonics patterns, syllable constructions, sight words, word families, morphological regularities and more.
By 6 - 7 years of age, a child is experiencing direct instruction in letter-sound relations (phonics) as well as practice in their use. He or she is reading simple stories using words with these phonic elements as well as high frequency words. By ages 7 - 8, direct instruction extends to include advanced decoding skills along with wide reading of familiar, interesting materials that help promote fluency. Meanwhile, the child is being read to at levels above their own independent reading level to develop language, vocabulary and concepts (Chall, 1996). The child should be motivated to extend themselves in relation to both expressiveness and comprehension.
PRINT WORD(S) ---> DIVIDED INTO SYLLABLES & GRAPHEMES ---> SOUNDED OUT ---> RECOGNISED ---> VOICED FLUENTLY [EITHER AUDIBLY OR INAUDIBLY] ---> UNDERSTOOD IN CONTEXT
The sequence when reading words in isolation as well as those in connected text is:
- Do I see the word(s) and attend to the word(s)?
- Do I recognise it/them as one(s) I know? Do I recognise it/them immediately or do I need to decode it/them? Can I begin to guess it/them based on context and other cues? Do I simply recognise it/them or can I also sound it/them out?
- Can I "chunk it/them"? (e.g. identify syllables, onset-rime and graphemes)
- Can I allocate sound(s) to individual letters or letter combinations (e.g. graphemes)?
- Can I refine how the word or words are read in syllables and use my knowledge of patterns to read more proficiently and meaningfully?
- Can I recognise the word or words along with words around it/them (if applicable)?
- Can I re-read the word or words and the sentence (if applicable) with expression and confidence?
- Do I consider the meaning of the word, the current utterance and other potential utterances?
- Can the learner begin to develop a more systematic understanding of how English words work?
As learners firmly grasp the concepts of words, phonemes, graphemes and morphemes, then it becomes more feasible to systematically study graphemes in what would be called a synthetic manner. This would extend to involve further exercises which refine the learner's knowledge of spelling rules, stress patterns and more. For the moment, consider the following order of phonics to be taught in a synthetic manner (source: Bear, et al., 2015):
Letter Name-Alphabetic (Semi-Phonetic) Stage [typically between 4 - 7 yrs old]: CVC word patterns with the following sequence of graphemes and blends: short a, m, t, s, short i, f, d, r, short o, g, l, h, short u, c, b, n, k, v, short e, w, j, p, y, x, q, z, sh, ch, th, wh, st-, pl-, bl-, gl-, sl-, sp-, cr, cl, fl, fr, sk, qu, nk, ng, mp, ck
Within Word (Transitional) Stage [typically between 7 - 9 yrs old]: CVCe word patterns leading into more complex CVVC vowel patterns and common multisyllabic words: a-e, ai, ay, ei, ey, ee, ea, ie, e-e, i-e, igh, y, o-e, oa, ow, u-e, oo, ew, vowel+r, oi, oy, ou, au, ow, kn, wr, gn, shr, thr, squ, spl, tch, dge, ge, homophones
Syllables & Affixes (Independent) Stage [typically between 9 - 11 yrs old]: multisyllabic words, adding inflectional endings, homographs & homophones
Derivation (Advanced) Stage [typically between 11 - 14 yrs old]: focusing on advanced prefixes, suffixes, roots as well as word families (e.g. exclaim, exclamation, exclamatory)
In this model, learners become familiar with letter-sounds after they are supported to navigate sounds-to-letters. Furthermore, one is exploring language well before this or - at least - alongside this study. Upon recognising words from a string of letters and/or sounds, and pictures/intentions from a string of words, then there is hope that learners can process that which has been portrayed within the coded text as well as in the spoken stream. There is hope that one is informing and being informed; is entertaining and being entertained; is greeting and being greeted; etc.
Grapheme / Phoneme Charts
Part Three: Understanding
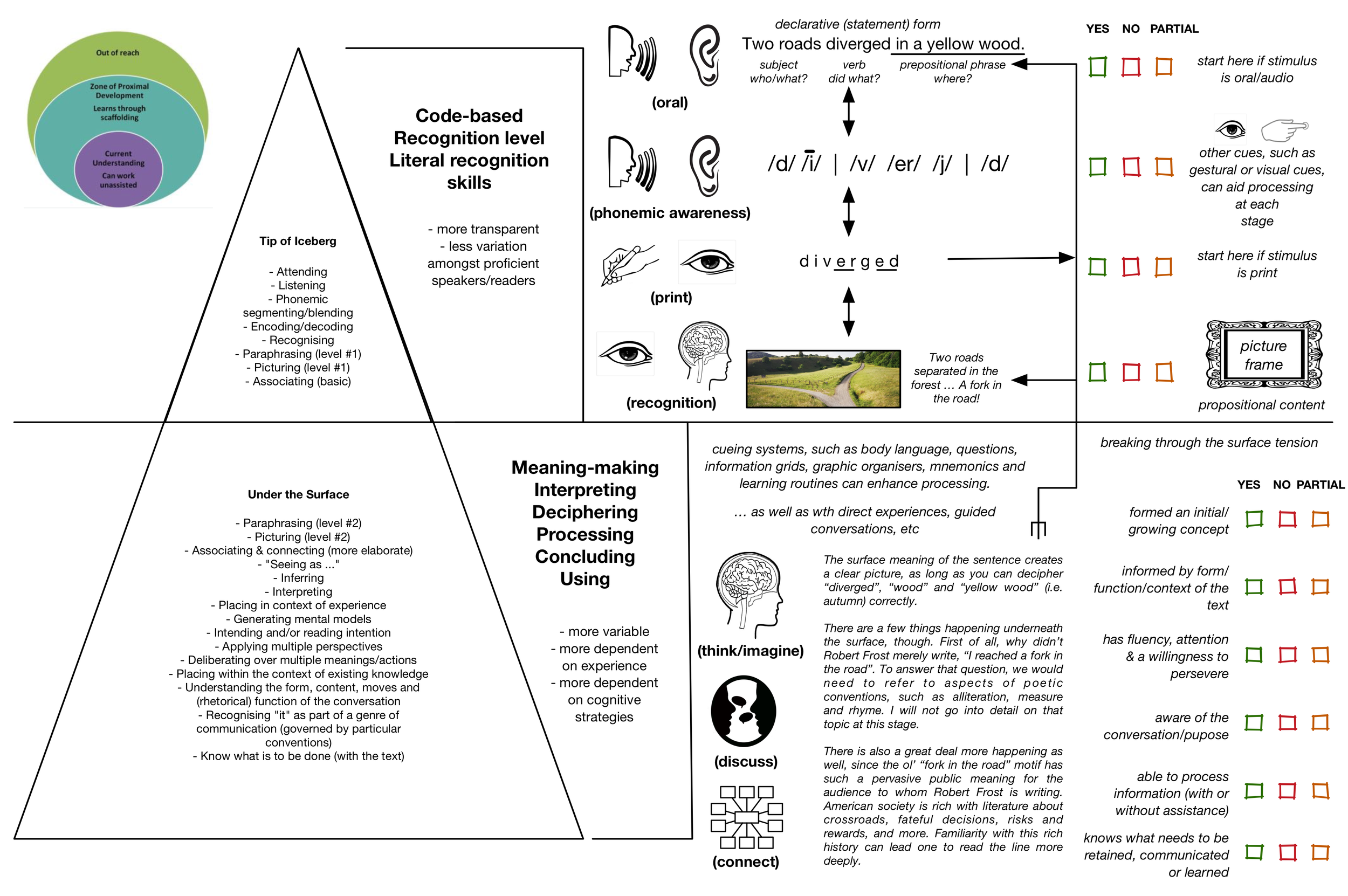
At this point, it is no longer enough to merely encode, decode and understand basic texts. One needs to encode, decode and understand diverse texts rapidly and accurately in order to read with enough fluency so as to make way for deep comprehension. This requires the learner to coordinate a range of skills, including attention, perception, language knowledge, background/contextual knowledge, phonemic awareness, phonics knowledge, word/morphological pattern recognition, sight word memory, grammatical knowledge, knowledge of text types and the ability to anticipate/select language based on this prior experience.
In this case, there is a text (perhaps spoken, maybe written). I recognise language/words in it (at least most of them). I know the context and the purpose of the text. I know what to look for. There are words that I may need to define in context or have explained to me. I can follow the logic/context, though. I can piece it together to make some logical whole. There are certain occasions where I may get stuck. For instance, I might need to clarify unfamiliar language. I might get stumped by a turn of phrase or two. I might lack some background knowledge or experience. I may just miss the point altogether. I may need the meanings of things explained to me. (What should I be thinking when I read this? What is meant/intended here?) Or I might need help sounding out more complex or unfamiliar terms. What I need most is daily practice which can lead to discoveries about the world, about language and about literacy.
When we process literate language, we process surface features for recognition AND we process deeper features to extract meaning. This is portrayed in the above Iceberg Metaphor.
A significant amount of experience is required to read and write in this meaningful manner. Without this, reading is like looking through a muddy window; you need to strain too hard to see clearly; you can only see things in bits, if at all. However, even if the window is clear (e.g. decodable) you still need to know what you are looking at and what you are looking for.
This reminds me of two parallel experiences of "learning to read". This first involved my stuttering attempts to read in a foreign language, albeit Spanish which shares many common features to English. My lack of vocabulary and insufficient grammatical knowledge meant that I regularly lost my train of thought when reading even the most basic of paragraphs, which - if presented in English - would have been easily comprehended, leaving much space to interpret and apply the information. However, in Spanish, I could not confidently interpret what I was reading, because I lacked confidence and clarity in exactly what I was decoding. I lacked adequate language knowledge.
A much different experience involved the poetry of e.e. cummings, a poet I adore but who I needed to learn to read ... or - rather - make sense of. In the case of e.e. cummings, I could easily recognise the language, yet it took time to make sense of cummings' innovations with linguistic and poetic forms. It took time to realise the intent behind his innovations, and to come to appreciate how he wanted me - his audience - to feel, think and envision. In order to better understand this latter experience, please explore the essay "To understand, you need to part of the conversation". In practice, reading requires limited background knowledge in the earlier years and substantial background knowledge and concepts as one progress through adolescence into adulthood.
Conclusion
What's the story, then? Our expectations change across time. That much is obvious.
"Word reading is the best predictor of reading comprehension level in the early years (Juel, Griffith & Gough, 1986); but others skills (e.g. background knowledge, inferring, summarising, etc) become more important predictors of comprehension level as word reading ability develops through experience (Curtis, 1980; Saarnio, et al., 1990). Thus, the relative importance of different skills may change during the course of development." (Cain, Oakhill & Bryant, 2004, p. 32)
There is a time when we are happy that a learner is exploring new words, is using language, is curious about letters and print, and is aware of sounds within words. There comes a time when we expect more, though. We expect learners to spell and read and write and talk more confidently and proficiently. Nothing more, nothing less. And - then - even this is no longer adequate. There comes a time when learners need to process information, organise and communicate thoughts, discuss with peers and synthesise one’s knowledge. We expect more because ...
“... literacy isn’t a single skill that simply gets better with age ... Being literate is very different for the skilled first grader, fourth grader, high school student, and adult, and the effects of school experiences can be quite different at different points in a child’s development.” (Catherine Snow, et al, 1991, pg 9)
Diligence, scaffolding, practice and challenging experiences are required. Nothing more, nothing less.
References
Bear, S., Invernizzi, M., Templeton, S., & Johnston, F. (2014). Words their way: word study for phonics, vocabulary, and spelling instruction (5th edition). Essex: Pearson.
Cain, K. E., Bryant, P. E., & Oakhill, J. (2004). Children’s reading comprehension ability: Concurrent prediction by working memory, verbal ability, and component skills. Retrieved from http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.96.1.31
Chall, J. S. (1996). Stages of reading development (2nd ed.). Fort Worth: Harcourt Brace Jovanovic College Publishers.
Curtis, M. E. (1980). Development of components of reading skills. Journal of Educational Psychology, 72, 656–669
Juel, C., Griffith, P. L., & Gough, P. B. (1986). Acquisition of literacy: A longitudinal study of children in first and second grade. Journal of Educational Psychology, 78, 243–255
Saarnio, D. A., Oka, E. R.,& Paris, S. G. (1990). Developmental predictors of children’s reading comprehension. In T. H. Carr & B. A. Levy (Eds.), Reading and its development: Component skills approaches (pp. 57–79). New York: Academic Press.
Snow, C. E., Barnes, W. S., Chandler, J., Goodman, I. F., & Hemphill, L. (1991). Unfulfilled expectations: home and school influences on literacy. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
The pupil must want to go on alone in taking language to the world
I can't seem to shake a preoccupation that continues to surface whenever I try and come to some synthesis of literacy. I am dogged by a persistent dichotomy. On the one hand, literacy is a skill to be mastered, which involves the methodological development of the formal characteristics of language and of the written code. On the other hand, literacy is a creative, communicative practice that calls upon the imagination, the intellect and social cognition, which is much less mechanical and much more about craft, application and growing expertise.
So ... whilst a learner may master the mechanical features of literacy through practice, revision and integration, the applied aspects of literacy require one to negotiate concepts of context, convention, intention, prior knowledge and (possible) meanings, which are not so formally defined.
This integration of form with intention reflects remarks from British philosopher Ray Monk (1999):
"The reason computers have no understanding of the sentences they process is not that they lack sufficient neuronal complexity, but that they are not, and cannot be, participants in the culture to which the sentences belong. A sentence does not acquire meaning through the correlation, one to one, of its words with objects in the world; it acquires meaning through the use that is made of it in the communal life of human beings."
The following "diagram" tries to broach the dichotomy once again. On the left hand side, there are the formal elements of language and literacy. On the right hand side, there are the functional areas to which language and literacy are put to use. And down the centre are quotes which move from a focus on mastery to a focus on application.
Consequently, language and literacy are much more than the mastery of a technique, even though mastery is a significant component of early literacy. The philosopher Rush Rhees (2006) grapples with this temptation to see language as a set of self-contained skills:
"The people who argued with Socrates and Plato may have thought language was just a collection of techniques, and that that was what understanding is: knowing the technique ... For them, the growth of understanding could only mean the growth of skill (efficiency, I suppose) or the multiplication of skills ... A skill would have the sort of unity that a calculus does ... Is understanding just competence?" (pg. 3)
By ending with a rhetorical question, Rhees is expressing some doubt in the idea that understanding is simply a measure of technical proficiency alone. Learning how to spell can be considered to be a technical skill. Knowing how to parse a sentence is also a technical exercise. Yet understanding and communicating are much more complex than technical prowess,
"If you understand anything in language, you must understand what the dialogue is, and you must see how understanding grows as the dialogue grows ... For language is discourse, is speaking. It is telling people things and trying to follow them. And that is what you try to understand ... You understand when it adds to your understanding of the discussion. Or of what the discussion is about." (Rhees, 2006, pg. 7)
At the same time that one is mastering elements of language and literacy, one must be granted opportunities to put these elements into practice, such as through interactive writing, scaffolded discussion, dialogic reading, poetry clubs, anchored instruction, literature circles, the language experience approach and more. In doing so, life is breathed into what would otherwise be cold and lifeless. Whilst it may be convenient to see literacy as a set of skills that are built progressively and mechanically, we must remind ourselves (as Stanley Cavell reminds us),
“The pupil must want to go on alone in taking language [and literacy] to the world, and that what is said must be worth [saying and writing], have a point (warning, informing, amusing, promising, questioning, chastising, counting, insisting, beseeching, specifying the location of pain, and so on) .. If it is part of teaching to undertake to validate these measures of interest, then it would be quite as if teaching must, as it were, undertake to show a reason for [communicating] at all.” (Cavell, 2005, pg 115)
Garver (1996) suggests that the shifting of attention between matters of form and matters of function is no simple act. They represent quite different paradigms.
“If Wittgenstein and Saussure agree in using ‘grammar’ descriptively, they disagree about ... other matters. One is that Wittgenstein’s grammar has to do with uses of language (discourse conditions and discourse continuation) rather than forms and their combinations (morphology and syntax) ...
"Considering uses rather than forms is a deep rather than a superficial departure from classical linguistic methodology ... Studying uses of language makes context prominent, whereas the study of forms lends itself naturally to analysis.” (Garver, 1996, pg 151)
Formal theories of meaning seek to explain how a language expresses a sense through an understanding of the language's logical structure. One must have access to the phonetic, syntactic and lexical knowledge to be able to decode sentences and to decipher the pictures expressed by them. This process is an analytical exchange. In a purely formal account of meaning, the individual would only be required to calculate the exact, unambiguous meaning of a proposition from available signs as long as the proposition was logically expressed and all terms were accounted for clearly and directly.
Meaning-in-context, on the other hand, is less static and more elusive. The meaning of an utterance requires an understanding of its context, a familiarity with the way the utterance is being exchanged, the intention of the utterance, and the position of the utterance within a 'language game' or 'conversation'. Such a theory of meaning must take into account that the subject is a creative, imaginative agent who extends (or projects) new language practices from prior encounters, and that such meaning is framed by the individual's social and discourse practices. Becoming literate also requires that one incorporates the role of “textuality” into one’s life, such as writing lists, emails, letters, notes, poems, etc. And it is bolstered when one experiences positive encounters of meaning making (and learning) with others (e.g. sharing a favourite book with someone you respect).
If I am able to allude to a final theorist here, this dynamic exchange of meaning-making is what Bakhtin (1981) refers to as the dialogic imagination. And it is the dialogic imagination that propels the text (or the logic of a text) forward. In other words, it is an explicit or implicit awareness of the underlying dialogue and associations - made up of questions, expectations, motifs, and conventions - that provide the rationale for the shape and significance of a text. Even as a text struggles to be unique, it exists within the frame of prior conversations and experiences. The more familiar one is with certain activities and conversations - or the text's semiotic domain/context - the deeper one will engage with and comprehend the text (Gee, 2003). If this is done in language that is accessible to the learner, then the possibilities for deep learning are extended even further. In this case, the lower order skills of word/sentence recognition are processed more deeply within the higher order skills of verbal reasoning, prior knowledge and extra-rationale interpretation.
What - then - is the point of this long-winded musing? In one sense, it is the continuation of a long-running discussion of the importance of balancing code-based and meaning-based practice. Those who are familiar with this site will see how this discussion features regularly. On another hand, I would like to return to the statement quoted in the title "the pupil must want to go on alone in taking language to the world." In other words, effective teaching builds skills AND provides rich, motivating opportunities to use these skills in committed acts of communication. This adds something even more elusive to the mix: as teachers, we must inspire learners to read, write, speak, listen, learn and express.
References
Bakhtin, M. (1981). The Dialogic Imagination. Austin: University of Texas Press.
Cavell, S. (2005). Philosophy the day after tomorrow. In Philosophy the day after tomorrow (pp. 111 – 131). Cambridge, MA: Belknap Press.
Garver, N. (1996). Philosophy as grammar. In H. Sluga & D. Stern (Eds.), The Cambridge companion to Wittgenstein (pp. 139 – 170). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Gee, J. P. (2003). Opportunity to learn: a language-based perspective on assessment. In Assessment in Education: Principles, Policy and Practice, Vol 10, No. 1, pp 27 - 46
Monk, R. (1999, July 29). Wittgenstein’s Forgotten Lesson. Prospect Magazine. Retrieved from http://www.prospectmagazine.co.uk/magazine/ray-monk-wittgenstein/#.Uo_n_pHqvGY
Rhees, R. (2006). Wittgenstein and the possibility of discourse (2nd ed.). Oxford, UK: Blackwell Publishing.
New Reading Lists Added to The Literacy Bug: Stages of Literacy Development
It is with great pleasure that we make this small - yet important - update. We would like to announce that we have categorised some of our recommended references according to Jeanne Chall’s Stages of Reading Development. Regular visitors would be well aware that Chall’s model plays an important role in The Literacy Bug’s approach to literacy teaching and learning. If you are not familiar with Chall’s model, we encourage you to read the linked essay on the Stages of Literacy Development and/or visit the notes on the Five Stage of Reading Development.
Otherwise, proceed straight to the newly added reading lists. Each list begins with a brief description of the stage.
Stage 0: Pre-Reading: Birth to 6 Years Old
In Stage 0, the child pretends to read, gradually develops the skills to retells stories when looking at pages of books previously read to him/her. The child gains the ability to name letters of the alphabet, prints own name and plays with books, pencils and paper. By six years old, the child can understand thousands of words but can read few (if any). In this stage, adults are encouraged to scaffold child’s language attempts through parallel talk, expanding on verbalisations and recasting child’s verbalisations. Adults are encouraging children to use of two to three word combinations within social contexts, and adults should implement dialogic reading or effective shared reading for young children ages 2 to 5 years. Any instruction (phonics, vocabulary) should be linked to the book reading, and such books should include rhyme, alliteration, and repetitive phrases. In one’s environment, adults should verbally label objects with which children are involved and encourage children to ask questions and elaborate on observations (Westberg, et al., 2006). Click here to explore recommending readings for Stage 0.
Stage 1: Initial Reading & Decoding: 6 to 7 Years Old
In Stage 1, the child is learning the relation between letters and sounds and between print and spoken words. The child is able to read simple texts containing high frequency words and phonically regular words, and uses skills and insight to “sound out” new words. In relation to writing, the child is moving from scribbling to controlled scribbling to nonphonemic letter strings. Adults are encouraging the child to write about known words and use invented spellings to encourage beginning writing, which can be extended through assisted performance. In this stage, the main aims are to further develop children’s phonological awareness, letter-sound knowledge, and ability to manipulate phonemes and syllables (segmentation and blending). (Westberg, et al., 2006) Click here to explore recommending readings for Stage 1.
Stage 2: Confirmation & Fluency: 7 to 9 Years Old
In Stage 2, the child can read simple, familiar stories and selections with increasing fluency. This is done by consolidating the basic decoding elements, sight vocabulary and meaning context in the reading of common topics. The learner’s skills are extended through guided read-aloud of more complex texts. By this stage, adults should be providing instruction that includes repeated and monitored oral reading. Teachers and parents must model fluent reading for students by reading aloud to them daily and ask students to read text aloud. It is important to start with texts that are relatively short and contain words the students can successfully decode. This practice should include a variety of texts such as stories, nonfiction and poetry, and it should use a variety of ways to practice oral reading, such as student-adult reading, choral (or unison) reading, tape-assisted reading, partner (or buddy) reading and reader’s theatre. (Westberg, et al., 2006) Click here to explore recommending readings for Stage 2.
Stage 3: Reading for Learning the New: 9 to 13 Years Old
In Stage 3, reading is used to learn new ideas, to gain new knowledge, to experience new feelings, to learn new attitudes, generally from one or two points of view. There is a significant emphasis placed on reading to learn, and writing for diverse purposes. There is time spent balancing the consolidating of constrained skills (spelling, grammar, fluency) whilst providing ample opportunities to explore topics through reading, writing, speaking, listening & viewing. By this time, the learner has transitioned to a stage where he or she is expected to learn from their reading. Adults should teach specific comprehension strategies, such as comprehension monitoring, using graphic and semantic organisers, answering questions, generating questions, recognising textual structures, summarising, and identifying main ideas and important details. (Westberg, et al., 2006) Click here to explore recommending readings for Stage 3.
Stage 4: Synthesising, Critiquing & Applying Perspective: 13 to 17 Years Old
In Stage 4, learners are reading widely from a broad range of complex materials, both expository and narrative, and are asked to apply a variety of viewpoints. Learners are required to access, retain, critique and apply knowledge and concepts. Learners are consolidating general reading, writing and learning strategies whilst being required to develop more sophisticated disciplinary knowledge and perspectives. These adolescent learners deserve content area teachers who provide instruction in the multiple literacy strategies needed to meet the demands of the specific discipline. In these areas, adolescents deserve access to and instruction with multimodal as well as traditional print sources. (International Reading Association, 2012). Click here to explore recommending readings for Stage 4.
We hope the newly added lists are helpful. If you would like to provide any recommendations or send us a comment, please do not hesitate to contact us at info@theliteracybug.com or use the comment box/link below.
References in this blog entry
International Reading Association. (2012). Adolescent Literacy: a position statement of the International Reading Association. Newark, DE.
Westberg, L., McShane, S., & Smith, L. (2006). Verizon Life Span Literacy Matrix: Relevant Outcomes , Measures and Research-based Practices and Strategies. Washington D.C.
A story that cuts right to the heart of the Opportunity to Learn issue
I have mentioned it before and it is a concept that I will return to again and again; the issue of equality in opportunity to learn. Today, I thought I’d spend some time reflecting on a short story I once wrote that relates directly to the main topic: considering whether all learners have equal opportunity to learn and succeed.
You won’t have a chance to read the actual story. It is stored somewhere so safe that the best minds are yet to uncover it. You must instead rely upon my synopsis. As far as the setting, the story takes place in inner city San Diego in the late 1990s. It is a low socio-economic community with issues common to the time: drugs, gangs, racial tensions and the working poor. I was teaching at a high school in the community when I wrote the story.
The story itself is an appropriation of “Eveline” by James Joyce. In Joyce’s tale, the main character - Eveline - is a young woman who is sitting forlornly in front of a dilapidated house in a crowded street in Dublin. Her mother has passed away, and she left behind a baby girl, Eveline’s sister. Eveline’s brothers have moved out of home, her father is a drunkard, and she is now responsible for raising her baby sister whilst working part-time and avoiding her father’s abuse. Her opportunities are fairly limited by poverty, circumstance and the expectations placed on a woman of the times (early 1900s).
In the story, Eveline is approached by a “fellow” who confesses his love for her, and promises to take her away from this misery and start a new life overseas. We might expect her to rush towards this door of apparent freedom, but she doesn’t. At the critical moment where she is to board a ship bound for the New World, she stands frozen on the docks and she watches the fellow leave her behind. We don’t know if she stays due to a promise she made to her mother - "to hold the house together" - or her fear that she would face another type of servitude as a wife in a foreign land. Eveline’s opportunities are severely limited by complex factors, which serve to paralyse her.
In my appropriation - “Jinicia Sings the Blues” - my main character - Jinicia - is a young African American women - aged 18 or so - leaning on a railing outside her house, watching her younger brother deftly navigate a local game of street soccer. Inside the house, Jinicia’s baby sister is asleep. Her dedicated father is at work, and he works three jobs just to pay the bills. Her mother left the family with another man. And her older brother was shot dead in a gangland dispute a couple years ago. Meanwhile, Jinicia watches her younger, talented brother with a mixture of pride, envy and pity. He is good at school, good at sport and is a born leader. She wants him to dribble the ball down the block and out of the neighbourhood and never look back. She is afraid that the community will eventually swallow him up in some minimum wage job or worse, and that the dream of a scholarship to college will be left unrealised. Jinicia is a clever young woman who wavers between hope and fear, and can’t help battle a deep cynicism. The story ends as she walks back into the house to cradle her waking sister, who she also looks upon with both love and trepidation.
At one stage, I entertained the thought of extending the story. I thought of introducing a character from the other side of the tracks, or across the bridge in the wealthy peninsular community of Coronado. I imagined Jinicia reflecting on the differences in the two worlds. She wouldn’t be able to stop herself from thinking, “would my older brother still be alive if we could have bailed him out of his trouble? would I even worry about my younger brother if our circumstances were different?”
I think the story cuts right to the heart of the Opportunity to Learn issue. Whilst the story might not be about literacy, it engages with an issue raised by Donaldo Macedo, “reading specialists … who have made technical advancement in the field of reading … [must] make linkages between their self-contained technical reading methods and the social and political realities that generate unacceptably high failure reading rates among certain groups of students.” (Macedo, 2001, pg xiii)
If the components of reading development are known (National Reading Panel and others), why is it that success rates are directly linked to differences in socio-economic factors and not to differences in cognitive functioning or personal motivation? (Chiu, McBride-Chang & Lin, 2012) We need to know, “the sociological processes which control the way the developing child relates himself to his environment. It requires an understanding of how certain areas of experience are differentiated, made specific and stabilised … What seems to be needed is the development of a theory of social learning which would indicate what in the environment is available for learning, the conditions of learning, the constraints on subsequent learning, and the major reinforcing process.” (Bernstein, 1964, pg. 55)
As stated by James Paul Gee, “caring about [students’] rights means caring … about the trajectories of learners as they develop … as part of communities of practice, engaged in mind, body, and culture, and not just as repositories of skills, facts, and information.” (2008, pg 105) We must be ever diligent on issues of equity, both in enhancing opportunities and respecting diversity. We must be conscious of the socioeconomic, motivational and neurocognitive factors that are brought to bear on learning. We must be mindful of the impacts of poverty, discrimination and instability. The conditions for success are multifaceted, long and intricate.
References
Bernstein, B. (1964). Elaborated and Restricted Codes: Their Social Origins and Some Consequences. American Anthropologist, 66(6_PART2), 55–69.
Chiu, M. M., McBride-Chang, C., & Lin, D. (2012). Ecological, psychological, and cognitive components of reading difficulties: testing the component model of reading in fourth graders across 38 countries. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 45(5), 391–405.
Gee, J. P. (2008). A sociocultural perspective on opportunity to learn. In P. Moss, D. Pullin, J. P. Gee, E. Haertel, & L. Young (Eds.), Assessment, equity, and opportunity to learn (pp. 76 – 108). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Macedo, D. (2001). Foreword. In P. Freire (Ed.), Pedagogy of freedom: ethics, democracy and civic courage (pp. xi – xxxii). Maryland: Rowman & Littlefield Publishers.
Change is technically simple and socially complex
I think I have driven myself mad on the topic of literacy. I do not exaggerate. The opening statement is not meant to be a rhetorical device. I mean, I just completed a sizeable pile of notes, diagram and essays which all centre around the following two questions:
- What is the sequence of skills developed across the stages of literacy development? and
- How do we as policy makers, teachers, parents, and community members arrange the right instruction at the right time with the right resources so learners are developing toward rich, diverse literacy practices?
I've also recently finished an online course with eminent literacy academic Catherine Snow, which was inspiring and insightful as well as being challenging for all participants.
So ... every diagram, lesson, assessment and lecture that I view, read or write appears to help resolve the above questions from me, yet at the same time these resolutions do not immediately impact on the lives of learners that I have in the forefront of my mind: the refugee children and indigenous children which I regularly have come into contact with. What we require are daily activities of challenging learning with high support that are based on a keen understanding of the learner’s developmental trajectory.
However, this is easier said than done. As I once read (Spark, 2003), “change is technically simple and socially complex”. Doesn’t that hit the proverbial nail on the head!
So I need to remind myself of something I wrote in the essay entitled Never forget language and literacy are learned with steady guidance from others. In that essay, I told myself that there are no silver bullets, there are no quick fixes and there are no jumping the queue when it comes to the gradual development of strong language, literacy and learning practices. A learner requires instruction that is based on quality teaching with quality resources in quality spaces through quality relationships with a clear understanding of the learner’s needs. Easy! Right?
There is a certain degree of pressure to gain skills in a timely manner. And learners benefit from the time and enabling environments to gain a command of the salient features of language to build confidence in certain familiar uses of language, literacy and also numeracy before being faced with more advanced forms, content and uses. Learning language and literacy are technical achievements. Sure! Right?
But at the same time, Stanley Cavell reminds us that this learning is initially grounded in the compulsion to know and to communicate. First, he stated, ”[we] forget that we learn language and learn the world together” (Cavell, 1969, pg 19). Second, he stated “the pupil must want to go on alone in taking language to the world, and that what is said must be worth saying [and writing], have a point (warning, informing, amusing, promising, questioning, chastising, counting, insisting, beseeching, and so on) … If it is part of teaching to undertake to validate these measures of interest, then it would be quite as if teaching must, as it were, undertake to show a reason for speaking [writing and reading] at all.” (Cavell, 2005, pg 115)
So … these budding learners need to become skilled, practiced, knowledgable, capable, curious, trusting and confident regardless of their age. This goal is technically simple and socially complex. Or as Donaldo Macedo (2001) wrote, “reading specialists … who have made technical advancement in the field of reading … [must] make linkages between their self-contained technical reading methods and the social and political realities that generate unacceptably high failure reading rates among certain groups of students.” (pg xiii)
There are no quick fixes. There are no easy solutions. What is the way forward from here?
References
Cavell, S. (1969). Must We Mean What We Say?. New York: Charles Scribner’s Sons.
Cavell, S. (2005). Philosophy the day after tomorrow. In Philosophy the day after tomorrow (pp. 111 – 131). Cambridge, MA: Belknap Press.
Macedo, D. (2001) Foreword. In P. Freire, Pedagogy of freedom: ethics, democracy and civic courage (pp. xi - xxxii). Maryland’s: Rowman & Littlefield Publishers.
Sparks, D. (2003). Interview with Michael Fullan: Change agent. Journal of Staff Development, 24(1), 55-58.
Updates Galore! New pages, assessment advice and teaching strategies at The Literacy Bug
Wow! It has been far too long since the last update to The Literacy Bug's Journal. I dare not ask when the last update was. Despite the long silence - or perhaps to explain it - we have some significant updates to share with you.
Firstly, a new section has been added to the site, and it is called Developing. In this section, you will find advice on how to help students grow in the various skills that underpin literacy development, such as oral language, phonological awareness, fluency, comprehension and more. At the moment, there is only one page in the new section, and it is called Developing Constrained Skills, which are things like print awareness, phonemic awareness, decoding and spelling. Follow this link to find out more ...
There is also a new page in the Planning section: Using Quality Assessment Practices. Effective instruction is creative, challenging and targeted. This is why strong assessment practices before, during and at the end of teaching cycles are key to informed educational practices. We believe the new page is an essential addition to the site, and it complements the Balancing Instruction and Stages of Development pages very well. Check it out!
Regular visitors will notice that a couple pages from the Essays section have made their way into the Planning folder. They are An Initial Framework for Literacy Instruction and Literacy Development Requires Steady Guidance. Explore these old favourites when you have a chance. An old blog entry has also made its way into the folder: Key Questions to Guide Instruction. Last but not least, two related pages have been updated and we are very happy with the results: Establishing (Literacy) Practices and Why Do We Do What We Do?.
All in all, there is much to explore at The Literacy Bug (and I haven't even mentioned updates to the Recommended Readings and the Recommended Links pages). We hope you enjoy all the new stuff. Please explore!
Ensuring Equity in Opportunity to Learn
The following are elements that contribute to equality in the opportunity to learn. In an equitable system, all students would have access to:
- Engaged time;
- Quality teaching, resources and environments;
- Safe environments which students are free from harm and discrimination and that their basic needs are met;
- The material, cultural and economic means to achieve;
- Opportunities to practice and to extend practices;
- High expectations that are shared between the school and the home contexts;
- Suitable collaboration between the home and school contexts as well as with the broader community context;
- Schools and communities which are sensitive to the linguistic and cultural diversity of the student population, particularly when a minority of learners come to classrooms with a home language that is not used as the language of instruction;
- Instruction which is suitable to the learners’ stages of development, and learners have been given strategic skills that help them engage in the current and subsequent stages of learning;
- Learning environment which facilitate high challenge/high support instruction so that diverse students can make suitable and competitive progress;
- Special accommodations that have been made to meet the specific learning needs of all students;
- Content which is engaging, relevant, purposeful and that will build on prior knowledge and that will be consistent with current ways of knowing and be applicable to everyday problem-solving.
- An education that responds to individual affinities/talents so learners are able to capitalise on these interests and learning trajectories;
- Effective support in managing transitions between schooling/learning contexts;.
- Every opportunity to achieve, so that children's resilience is being developed and their motivation is fostered;
- Institutions and society that seek to minimise and mitigate the impacts of social and economic disadvantage; and
- People and institutions who keep “a finger on the pulse” of all students at all times. Progress is monitored, opportunities are made available, and extra support is facilitated, where required.
Welcome to The LITERACY BUG!!
The time has come! We enthusiastically welcome you to something we have been anticipating for some time … the launch for The Literacy Bug. So … please … say “HELLO” to Ludwig, a little bug who always has his head in a book.
Even though this launch comes with a fair amount of celebration, I must admit that it also comes with a teeny, tiny bit of sadness … not much … just a small morsel of it. I am compelled to remind myself that “we are NOT saying goodbye to Wittgenstein on Literacy or Wittgenstein on Learning.” The core spirit of the old name(s) will remain. It is not possible to severe the site’s deep ties to the philosophy of Ludwig Wittgenstein. After all, Wittgenstein was deeply fascinated by the diverse ways that language and literacy are used between people in the general course of living, imagining, conceptualising, doing, knowing, speculating, calculating, relating, etc. Perhaps the change of name is just a clever ploy and the discussion will go on as usual. To a certain extent, I think it will.
Nevertheless, exciting possibilities lay ahead. I look forward to expanding the literacy resources available on the site: links to fantastic online resource, lesson plans and ideas, great books for all ages and interests, and tips and tricks to help readers and writers as well as teachers and students. While I will miss having a little corner of the Internet carved out explicitly for the discussion of a certain application of Wittgenstein’s manner of approaching language, I couldn't honestly continue to act under the title Wittgenstein on Literacy/Learning when the conversation was moving more and more into a direct and contemporary discussion of literacy learning and instruction. So I must let the original (2007) premise of website evolve into what we have now and will have in the future.
The truth of the matter is this ... I may - in fact - be allowed to be more Wittgensteinian (without feeling the need to explicitly link observations to Wittgenstein). I may be freed to discuss a range of literature (children’s, young adult and more) with a keen eye on how readers and authors co-construct meaning based on certain shared assumptions. I may be better positioned to marvel at the developmental leaps that learners make as they grow through the various stages of literacy learning. I may be better able to provoke visitors to reconsider how our environments, practices, relationships and politics influence the potential for learners to catch the literacy bug and - thereby - take charge of their intellectual journey.
In the end, literacy is wide ranging phenomenon. What it means to a two year old and a four year old is different to what it means for a ten year old, a sixteen year old, a twenty year old, a thirty-five year old, a fifty year old and more. What it means now is different than what it meant thirty years ago and what it will mean in forty years time. The shape of literacy practice in urban Chicago is different to the role it plays in remote Australia which is different to the texts, contexts and traditions encountered by present-day youth in Cairo. That said, there is the old saying ... the more thing change, the more they remain the same.
Nevertheless, I am getting well ahead of myself. Welcome to The Literacy Bug … a little creature with the capacity to fly, burrow, nest, transform, whiz about and inspire. Please visit the new home page for a fresh discussion of the road ahead and subscribe to receive regular updates. And whilst you are here, stop by the site’s many familiar places: the themed notes, the key essays, the teaching principles, the reading lists and the glossaries. Welcome! Explore and enjoy!
Suggested Readings in Each of the Main Areas of Literacy Instruction
In an initial journal entry and past discussions, we identified that full literacy development required the parallel development of skills in the following areas:
- Robust development of oral language in language-rich and literacy-rich environments;
- Clear, systematic and intensive development of phonemic awareness;
- Further systematic and progressive development of alphabetic skills, including phonics, spelling and morphology;
- Wide ranging support of vocabulary development from a very young age;
- Expert utilisation of read-alouds;
- Skilled orchestration of language experiences;
- Substantial time set aside for fluency practice (include time for independent reading);
- Attention to ultimate goal of reading instruction: comprehension; and
- Apprenticeship into the craft of composition; and
- Ongoing and deepening construction of knowledge (the real goal of learning).
In a subsequent entry, we identified research-based techniques and activities that were found to build competencies in each area. At the end of that entry, we mentioned that we would soon share a selection of readings (e.g. journal articles and books) which explore instructional practices and principles in greater details. This entry fulfils this promise. Follow the "Read More" link for the list of recommended readings.
Read More